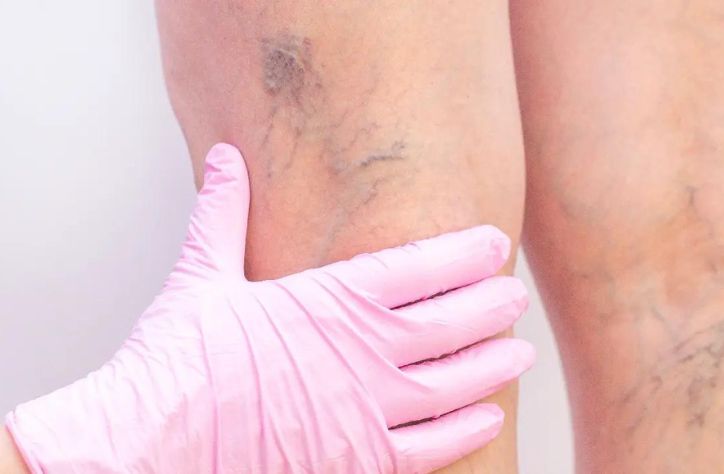
Have you ever glanced at your legs and wondered about those ropy, blueish veins snaking beneath the surface? Those bluish, bulging veins on your legs aren’t just a cosmetic issue. You may have probably heard of varicose veins, but do you know what they are and when they might pose a problem?
Let’s look closer at varicose veins, understanding what causes them, who’s prone to them, and when they cross the line from a nuisance to a health concern. By the end of this post, you’ll be equipped to recognize when those bothersome veins need professional attention.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are twisted, enlarged veins that typically occur in the legs. They develop when the tiny valves inside the veins weaken, allowing blood to flow backward and pool. This pooling causes the veins to swell and bulge, creating the characteristic appearance of varicose veins.
Let’s get the idea in more simpler terms, Imagine a one-way street where traffic starts flowing in reverse. That’s essentially what happens inside varicose veins. The valves, which normally keep blood moving toward the heart, malfunction, leading to blood pooling and vein distension. These swollen veins are what we recognize as varicose veins.
Who’s At Risk?
Understanding the factors that increase your risk of developing varicose veins can empower you to take proactive steps for better vein health. While anyone can develop them, certain factors make some individuals more susceptible than others:
1. Family History:
If varicose veins run in your family, your chances of developing them are significantly higher. This suggests a genetic predisposition, meaning you might inherit weaker vein walls or valves.
2. Age:
As we age, our veins naturally lose some of their elasticity and strength. This wear and tear can contribute to valve dysfunction and the development of varicose veins. Most cases occur after age 40.
3. Gender:
Women are more prone to varicose veins than men. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can relax vein walls, increasing the risk. Additionally, hormonal birth control and hormone replacement therapy can also play a role.
4. Pregnancy:
The increased blood volume and pressure during pregnancy put extra stress on veins, especially in the legs. This can lead to the formation of varicose veins, which often improve after childbirth.
5. Obesity:
Carrying excess weight puts added pressure on your veins, making it harder for blood to flow efficiently. This increased pressure can weaken valves and contribute to varicose vein development.
Prevent heart problems before they start – Schedule a preventive checkup
Contact Us6. Prolonged Standing or Sitting:
Jobs or lifestyles that involve extended periods of standing or sitting can hinder blood circulation in your legs. This sluggish blood flow can strain veins and increase the risk of varicose veins.
7. Other Factors:
Other factors that may contribute to varicose veins include:
- Previous leg injuries or surgeries
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Smoking
- Chronic constipation
When Do Varicose Veins Become a Cause for Concern?
Certain signs and symptoms indicate they may be progressing or leading to complications. It’s crucial to pay attention to these warning signs and seek medical advice if you experience any of the following:
1- Persistent Pain or Discomfort:
Occasional achiness or heaviness in the legs is common with varicose veins. However, if you experience persistent pain, throbbing, or cramping, it could signal a more serious issue like a blood clot (superficial thrombophlebitis) or inflammation.
2- Skin Changes:
Changes in the skin around your varicose veins, such as discoloration (redness, brownish staining), hardening, or the development of ulcers (open sores), are warning signs. These changes may indicate impaired circulation and a higher risk of infection.
3- Swelling and Inflammation:
While mild swelling is sometimes normal, especially after long periods of standing, persistent or worsening swelling in the legs or ankles could indicate a deeper problem like a blood clot or vein inflammation (phlebitis).
4- Bleeding:
If a varicose vein ruptures, it can cause bleeding, which can range from minor to significant. It’s essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any bleeding from your varicose veins.
5- Blood Clots
Rarely, varicose veins can develop blood clots (superficial thrombophlebitis) which can be painful and tender. While these clots typically resolve on their own, they can sometimes extend into deeper veins, leading to a more serious condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which requires immediate medical treatment.
6- Beyond the Surface
In some cases, varicose veins can be a sign of an underlying condition called chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). CVI occurs when the valves in your leg veins don’t function properly, leading to impaired blood flow and a variety of symptoms, including varicose veins, leg swelling, skin changes, and ulcers. It’s crucial to diagnose and manage CVI to prevent further complications.
Is it OK to Leave Varicose Veins Untreated?
Over time, untreated varicose veins can worsen, leading to increased pain, aching, swelling, and fatigue in the legs. These symptoms can significantly impact your daily life and overall well-being.
(CVI), often associated with untreated varicose veins, can cause skin discoloration, dryness, and the development of venous ulcers. These slow-healing wounds can be painful, prone to infection, and significantly diminish your quality of life.
In rare cases, varicose veins can develop blood clots (superficial thrombophlebitis), which can be painful and tender. While usually not life-threatening, these clots can sometimes extend into deeper veins, leading to a more serious condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT can be life-threatening if a clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
The pain, discomfort, and cosmetic concerns associated with untreated varicose veins can take a toll on your self-esteem, confidence, and overall quality of life. Activities you once enjoyed may become difficult or even impossible due to leg pain and fatigue.
Prevent heart problems before they start – Schedule a preventive checkup
Contact UsTreatment Options Available For Varicose Veins
Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available for varicose veins, depending on the severity of your condition and your individual needs. At Atlantic Cardiovascular, our experienced specialists are dedicated to providing personalized care and tailoring treatment plans to your unique situation.
Sclerotherapy:
This involves injecting a solution into the varicose vein, which irritates the vein lining and causes it to collapse. The body then naturally absorbs the collapsed vein over time.
Laser Ablation or Radiofrequency Ablation:
These techniques use heat to seal off the affected vein, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins. Both procedures are minimally invasive and require little to no downtime.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy:
This involves removing smaller varicose veins through tiny incisions in the skin. It’s often used in conjunction with other procedures.
Vein Stripping:
This traditional surgical procedure involves removing the varicose vein through incisions. It’s typically reserved for larger varicose veins and may require a longer recovery period.
Words By Author
In conclusion, varicose veins are a common condition with varying degrees of severity. While they may start as a cosmetic concern, understanding their causes and recognizing when they become a health risk is essential. By staying informed and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can effectively manage varicose veins and safeguard your vein health for years to come.