You’re sitting at your desk, or maybe lying in bed, when suddenly—thump, thump, thump—your heart takes off like it’s running a marathon. You pause, hold your breath, and wonder if you’re on the brink of something serious.
If this scene sounds all too familiar, you’re not just imagining it. Hormonal shifts, whether from menopause, stress, or thyroid imbalances, can send your heartbeat spiraling. But before the panic sets in and you start searching frantically for answers, take a breath.
This guide will show you exactly why these palpitations happen and, more importantly, how to manage them safely. It’s time to take back control of your heartbeat and let peace replace panic.
What are Menopause Heart Palpitations?
Menopause heart palpitations refer to sudden and noticeable changes in the rhythm or speed of the heartbeat that often occur during the perimenopausal or menopausal phase of a woman’s life. These palpitations can make the heart feel like it’s racing, fluttering, or even skipping beats. While they can be alarming, they are typically not dangerous and are often linked to the hormonal fluctuations that accompany menopause.
Why Do They Happen?
During menopause, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes, particularly in the levels of estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen plays a crucial role in the cardiovascular system, influencing how blood vessels expand and contract and how the heart functions. When estrogen levels drop, the autonomic nervous system can become more sensitive, triggering symptoms like heart palpitations.
Additionally, other factors can contribute to menopause-related heart palpitations, such as:
- Hot Flashes: Often paired with palpitations, hot flashes can cause a sudden increase in heart rate.
- Stress and Anxiety: Hormonal imbalances can heighten stress response, which may amplify the perception and frequency of palpitations.
- Thyroid Function: The thyroid gland’s activity may be affected during menopause, potentially leading to irregular heart rhythms.
- Lifestyle Factors: Caffeine, alcohol, and certain medications can exacerbate palpitations during menopause.
How Do They Feel?
Menopause heart palpitations can vary in intensity and duration. Some women may experience a brief flutter, while others report sustained periods of a rapid or forceful heartbeat. It’s common to feel these sensations more noticeably at rest or during moments of heightened awareness, such as when lying down at night.
Are They Dangerous?
Most of the time, these palpitations are harmless and temporary. However, if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting, it is crucial to seek medical attention. These could indicate a more serious underlying condition unrelated to menopause.
In summary, menopause heart palpitations are often a normal part of the menopausal transition, linked to fluctuating hormone levels and other physiological changes. Understanding them is key to managing their impact on daily life and maintaining peace of mind.
What Causes Menopausal Heart Palpitations?
Menopausal heart palpitations are primarily caused by the complex hormonal shifts that occur as a woman transitions through menopause. Here’s a deeper look at the main contributing factors:
1. Fluctuating Estrogen Levels
One of the hallmark changes during menopause is a decrease in estrogen levels. Estrogen has a direct impact on the cardiovascular system, helping to maintain blood vessel elasticity and regulate heart function. When estrogen levels drop:
- The autonomic nervous system may become more sensitive, leading to an increased likelihood of irregular heartbeats.
- Blood vessel constriction can become more pronounced, contributing to changes in heart rate and palpitations.
2. Progesterone Imbalance
Alongside estrogen, progesterone also plays a role in heart rhythm. Imbalances in these hormones can trigger episodes of rapid or irregular heartbeats as the body adjusts to changing levels.
3. Adrenal Gland Response and Stress
Menopause can be a physically and emotionally stressful time, causing the body’s adrenal glands to respond by releasing more cortisol and other stress hormones. These hormones can stimulate the heart and increase the frequency of palpitations, especially during moments of heightened stress or anxiety.
4. Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
Hot flashes are common symptoms during menopause and are often linked with an increased heart rate. The sudden surge of heat is typically followed by a rapid heartbeat or palpitations, making these episodes more noticeable. Night sweats can similarly disrupt sleep and contribute to heightened awareness of heart palpitations.
5. Changes in Thyroid Function
Menopause can sometimes impact thyroid function, causing conditions like hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, which can result in an irregular or fast heartbeat. The thyroid and reproductive hormones share a complex relationship, and fluctuations in one can impact the other.
6. Lifestyle Triggers
Certain lifestyle habits or external factors can exacerbate heart palpitations during menopause, including:
- Caffeine and Alcohol: These can stimulate the heart and increase the likelihood of palpitations.
- Diet and Dehydration: Poor hydration and low blood sugar can trigger palpitations.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those for cold and allergy relief or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), may have side effects that include palpitations.
7. Lack of Sleep
Menopausal symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats often disrupt sleep, leading to sleep deprivation, which can stress the cardiovascular system and make palpitations more frequent or noticeable.
8. Physical and Emotional Stress
Menopause can increase sensitivity to both physical and emotional stress, amplifying the body’s natural response. This may lead to a stronger, faster heartbeat even during low-stress activities or periods of rest.
Who Is at Risk for Menopausal Heart Palpitations?
Women most at risk for menopausal heart palpitations include:
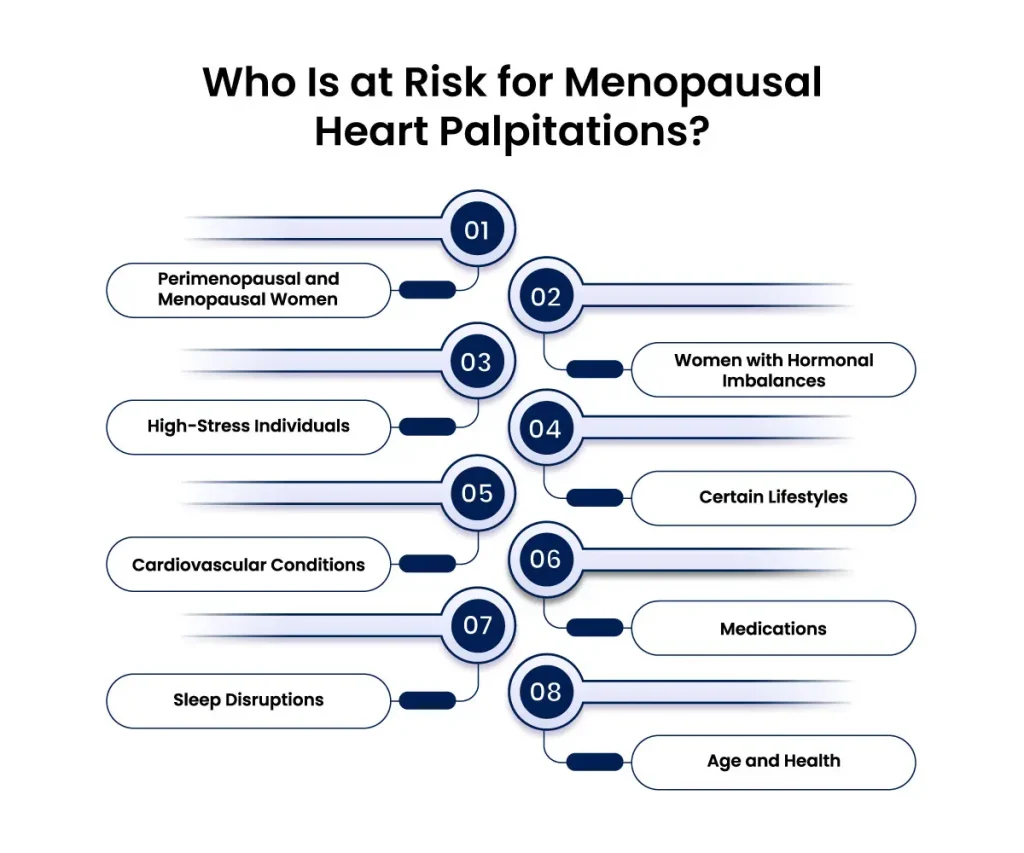
- Perimenopausal and Menopausal Women: Hormonal fluctuations during these phases can trigger palpitations.
- Women with Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders can increase susceptibility.
- High-Stress Individuals: Chronic stress or anxiety raises cortisol levels, impacting heart function.
- Certain Lifestyles: High caffeine/alcohol intake, smoking, poor diet, and inactivity can exacerbate palpitations.
- Cardiovascular Conditions: Those with existing heart issues or a family history of heart disease are at higher risk.
- Medications: HRT and stimulant-based medications can contribute to palpitations.
- Sleep Disruptions: Poor sleep, insomnia, or sleep apnea can stress the cardiovascular system.
- Age and Health: Women in their late 40s to early 50s or with poor overall health are more vulnerable.
What are Some Home Remedies To Help Manage Hormonal Palpitations?
Managing hormonal palpitations at home is possible with a few simple, non-medical remedies. Stress management is crucial, so incorporating deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the body and regulate heart rate.
Lifestyle adjustments like reducing caffeine and alcohol, staying hydrated, and eating a balanced diet with magnesium-rich foods such as leafy greens and nuts can make a difference. Regular meals help maintain stable blood sugar levels, which may prevent palpitations.
Gentle physical activity like walking, yoga, or tai chi supports cardiovascular health without overexertion. Prioritizing sleep is also essential; a consistent sleep routine and a cool, comfortable environment can help you rest better and reduce palpitations.
Herbal remedies like chamomile or valerian tea promote relaxation, while magnesium supplements can support heart health—always consult with a professional for proper dosage. Mind-body practices such as yoga, tai chi, or guided imagery are excellent for balancing the nervous system.
Avoiding known triggers, such as processed foods and late-night eating, can help reduce palpitations. Finally, staying connected with friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional comfort and reduce stress. While these methods can be effective, consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen to rule out other health issues.
Final Words
Heart palpitations are very common during menopause and don’t always indicate a serious heart issue. However, it’s important to discuss any cardiac symptoms with your healthcare provider. If your heart palpitations are related to menopause and are considered benign, menopausal hormone therapy may help by addressing estrogen withdrawal. Additionally, making lifestyle changes can help you manage and ease these symptoms.