So, you’ve just heard the words “100% blocked artery,” and naturally, a whirlwind of questions is running through your mind. What does it mean for your day-to-day life? How serious is it? And most importantly, what can you do about it? Let’s take a deep breath and break this down together. Understanding what to expect can make all the difference, so let’s explore this journey step by step.
Why Do Arteries Get Blocked?
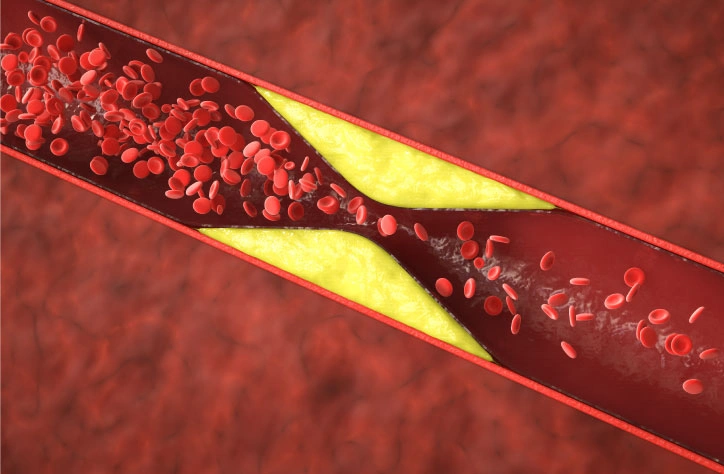
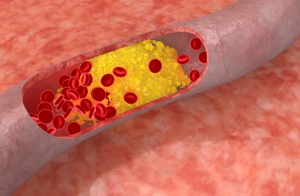
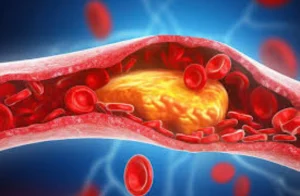
Blocked arteries are one of the most common heart health concerns, but why does it happen in the first place? The main culprit is a condition called atherosclerosis—a fancy term for something quite simple: the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances in your artery walls. Over time, this buildup, called plaque, narrows the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through.
Think of your arteries as highways for blood to travel. When atherosclerosis strikes, it’s like a traffic jam—slowing things down or stopping them completely.
Common Causes of Atherosclerosis
- High Cholesterol: When there’s too much bad cholesterol (LDL) in your blood, it can stick to the artery walls.
- Smoking: The chemicals in cigarettes damage your blood vessels, encouraging plaque buildup.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and sugar can accelerate the process.
- Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain and high cholesterol, two big risk factors.
- Diabetes and High Blood Pressure: These conditions can damage your arteries and speed up atherosclerosis.
What Is the Expectancy Rate With Blocked Arteries?
Blocked arteries, especially when left untreated, can have a significant impact on life expectancy. However, since many individuals remain unaware they have this condition, estimating its exact effects can be tricky. Studies suggest that a substantial percentage of middle-aged and older adults live with undiagnosed arterial blockages, which underscores the importance of early detection.
The primary cause of blocked arteries is atherosclerosis, a condition responsible for most cardiovascular diseases. While the specific impact on lifespan varies, research shows that the complications of atherosclerosis can dramatically shorten life expectancy:
- A heart attack may take over a decade and a half off your life.
- Developing heart failure often reduces lifespan by about a decade.
- Suffering a stroke can decrease life expectancy by nearly one-third.
These figures highlight how untreated arterial blockages can lead to severe, life-altering outcomes.
Factors That Influence Life Expectancy
- Location and Severity of Blockage:
A single artery blockage can sometimes be managed better than multiple blockages. Critical blockages in key arteries, like the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, may pose higher risks.
- Adaptation Through Collateral Circulation:
The body’s ability to develop alternative blood flow routes around the blockage can help prolong life, though it isn’t a guaranteed solution.
- Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments:
Medical interventions, such as stents, bypass surgery, or medications, often play a life-saving role. Additionally, lifestyle changes like improved diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can significantly boost both lifespan and quality of life.
How Do You Know If Your Arteries Are Blocked?
Blocked arteries often don’t announce themselves with loud, obvious symptoms. In fact, many people live with partially or fully blocked arteries for years without even realizing it. However, there are signs and tests that can help you uncover the condition before it leads to serious complications.
Common Symptoms of Blocked Arteries
Here are some warning signs to watch for:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort (Angina):
A tight, squeezing, or heavy feeling in your chest, especially during physical activity, can indicate reduced blood flow to your heart.
- Shortness of Breath:
If climbing stairs or walking short distances leaves you gasping for air, it may signal a blockage that’s affecting your heart’s ability to pump efficiently.
- Fatigue or Weakness:
Persistent exhaustion, even after light activities, might mean your heart isn’t getting the oxygen-rich blood it needs.
- Pain in Other Areas:
Blockages can also cause pain in the shoulders, neck, arms, back, or jaw, particularly during physical exertion.
- Leg Pain or Cramping (Claudication):
This is often a sign of blocked arteries in the legs (peripheral artery disease), which shares the same underlying causes as heart artery blockages.
Silent Blockages
In many cases, blockages don’t cause noticeable symptoms until they’re severe or cause a serious event like a heart attack or stroke. That’s why routine health screenings are so important, especially if you have risk factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, or a family history of heart disease.
How Are Blocked Arteries Diagnosed?
If you suspect you may have blocked arteries, your doctor can confirm it through several tests:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG):
Measures the electrical activity of your heart to identify potential issues with blood flow.
- Stress Test:
Monitors your heart’s performance during physical exertion to detect signs of reduced blood flow.
- Imaging Tests:
CT Angiography or Cardiac MRI can provide detailed images of your arteries to identify blockages.
- Angiogram:
A more invasive test where a special dye is injected into your blood vessels to pinpoint blockages on an X-ray.
- Blood Tests:
Elevated cholesterol or markers of inflammation may suggest a higher risk of arterial blockages.
What Are the Treatment Options for Blocked Arteries?
When it comes to treating blocked arteries, the approach depends on the severity of the blockage, your symptoms, and your overall health. Treatment typically focuses on improving blood flow, reducing symptoms, and preventing life-threatening complications like heart attacks or strokes. Let’s explore the most common options:
Medications
Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms, prevent further blockages, and reduce the risk of complications. Common options include:
- Statins: To lower cholesterol and slow plaque buildup.
- Blood Thinners: Such as aspirin, to reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Beta-Blockers and ACE Inhibitors: To manage blood pressure and reduce heart strain.
- Nitroglycerin: To relieve chest pain (angina) caused by blocked arteries.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For more severe blockages, procedures to restore blood flow may be necessary:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A catheter is used to open the blocked artery, and a small mesh tube (stent) is placed to keep it open.
- Atherectomy: A specialized device is used to remove plaque from the artery walls.
Surgical Options
In critical cases where minimally invasive techniques aren’t enough, surgery may be required:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Healthy blood vessels from another part of your body are used to create a bypass around the blocked artery.
- Endarterectomy: Plaque is surgically removed from the artery, often used for blockages in the neck (carotid arteries).
Managing Underlying Conditions
Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity can worsen blockages. Managing these effectively is a crucial part of treatment.
What’s the Right Option for You?
The best treatment for blocked arteries varies from person to person. Some may benefit from lifestyle changes alone, while others require a combination of medications and procedures. The key is early intervention—talk to your doctor to create a personalized treatment plan that suits your needs and improves your quality of life.
By taking proactive steps, you can manage blocked arteries and reduce the risks associated with them.
Words By Author
Blocked arteries are a serious condition, but they’re not a death sentence. With early detection, the right treatment, and lifestyle changes, you can manage the risks and improve your quality of life.
Whether it’s through medications, procedures, or healthier daily habits, taking proactive steps is the key to protecting your heart and your future. Always listen to your body and consult your doctor for guidance—your heart health is worth it!