Have you ever experienced that nagging ache in your legs and wondered if it was just varicose veins or something more serious like a blood clot?
Many people find themselves confused when searching for symptoms online, especially with terms like “deep vein thrombosis” popping up alongside varicose veins.
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the information and unsure about what’s really going on with your vascular health.
Imagine waking up with swollen, aching legs. Your first thought might be, “Is this just varicose veins, or could it be something more serious like a blood clot?” Understanding the difference is crucial—not just for your peace of mind, but for your health.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about blood clots and varicose veins. From recognizing the unique symptoms to knowing when to seek medical help, we’re here to provide you with clear, trustworthy information.
What Is A Blood Clot?
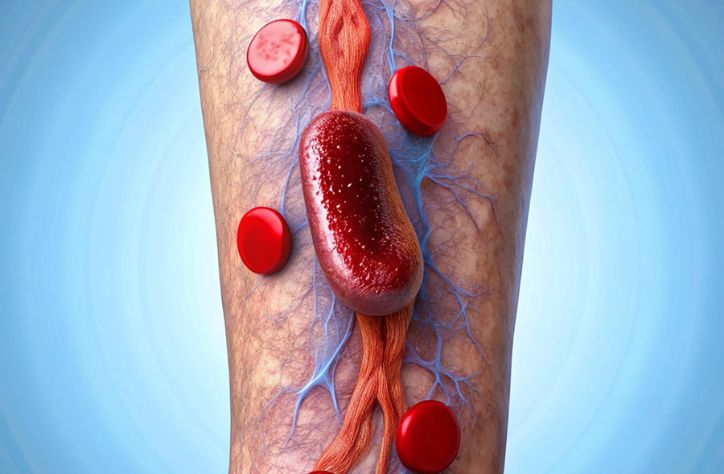
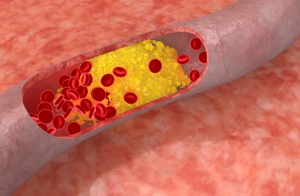
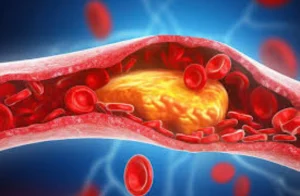
A blood clot is a gel-like mass formed by your blood when it changes from a liquid to a solid state. This process, known as coagulation, is essential for healing wounds and preventing excessive bleeding when you get injured. However, sometimes clots form inside your blood vessels without any obvious injury. When this happens, they can pose serious health risks.
There are two main types of blood clots:
- Arterial Clots: These form in the arteries, the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Arterial clots can block the flow of blood to vital organs, potentially leading to heart attacks or strokes.
- Venous Clots: These develop in the veins, which return blood to your heart. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common type of venous clot that usually occurs in the legs. If a part of this clot breaks off, it can travel to your lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called a pulmonary embolism.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins occur when the valves inside your veins don’t function properly. Normally, these valves help keep blood flowing in one direction—back to your heart. When they fail, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge and become visible through your skin. This pooling not only makes the veins appear swollen and twisted but can also lead to discomfort and other symptoms.
Prevent heart problems before they start – Schedule a preventive checkup
Contact UsCommon Characteristics of Varicose Veins
- Visible Veins: The most noticeable sign of varicose veins is their appearance. They often look blue or dark purple and can appear twisted or bulging.
- Aching and Heavy Legs: You might feel a persistent ache or heaviness in your legs, especially after standing or sitting for long periods.
- Swelling: Your legs and ankles may swell, particularly after extended periods of inactivity.
- Itching or Burning Sensation: Some people experience itching or a burning feeling around the affected veins.
- Cramps: Nighttime leg cramps are another common symptom associated with varicose veins.
Do Varicose Veins Cause Blood Clots?
You might be wondering, “Do varicose veins cause blood clots?” It’s a valid question, especially if you’re dealing with varicose veins and concerned about your vascular health. Let’s dive into this topic to clear up any confusion and provide you with the information you need.
Understanding the Connection
Varicose veins and blood clots both involve the veins in your body, but they don’t have a direct cause-and-effect relationship. However, having varicose veins can increase your risk of developing blood clots, particularly in certain circumstances. Here’s how they’re connected:
- Blood Pooling: Varicose veins occur when the valves in your veins don’t function properly, causing blood to pool and the veins to enlarge. This pooling can slow down blood flow, creating an environment where blood clots are more likely to form.
- Venous Stasis: The sluggish blood flow associated with varicose veins, known as venous stasis, is a key factor in clot formation. When blood doesn’t move efficiently, it can begin to clot more easily.
Prevent heart problems before they start – Schedule a preventive checkup
Contact UsKey Differences Between Blood Clots and Varicose Veins
| Aspect | Blood Clots | Varicose Veins |
| Definition | A gel-like mass formed by blood that changes from liquid to solid, blocking blood flow. | Enlarged, twisted veins that typically appear near the skin’s surface, usually in the legs. |
| Causes | – Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights, bed rest)- Surgery or trauma- Certain medical conditions (e.g., cancer, heart disease)- Genetic predisposition- Lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, obesity) | – Weak or damaged vein walls and valves- Age-related changes- Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., pregnancy, menopause)- Genetics- Prolonged standing or sitting |
| Common Locations | – Deep veins in the legs (Deep Vein Thrombosis)- Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism) | – Legs and ankles |
| Symptoms | – Swelling in the affected limb- Severe pain or tenderness- Red or discolored skin- Warmth in the affected area- Sudden shortness of breath (if clot travels to lungs) | – Visible, bulging veins- Aching or heavy feeling in the legs- Swelling- Itching or burning around the veins- Nighttime leg cramps |
| Risks and Complications | – Pulmonary embolism (life-threatening)- Stroke or heart attack (if arterial clot)- Chronic pain and swelling | – Skin ulcers- Blood clots in varicose veins- Bleeding from superficial veins- Chronic pain and discomfort |
| Diagnosis | – Ultrasound- Blood tests (e.g., D-dimer)- Venography- MRI or CT scans | – Physical examination- Ultrasound- Venography (in some cases) |
| Treatment Options | – Anticoagulant medications (blood thinners)- Thrombolytic therapy (clot dissolvers)- Compression stockings- Surgery (in severe cases) | – Lifestyle changes (exercise, weight management)- Compression stockings- Sclerotherapy- Laser therapy- Vein stripping or ligation |
| Prevention Strategies | – Staying active and avoiding prolonged immobility- Using compression stockings during long trips- Maintaining a healthy weight- Avoiding smoking- Managing underlying health conditions | – Regular exercise- Elevating legs- Wearing compression stockings- Maintaining a healthy weight- Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting |
| When to Seek Medical Help | – Sudden swelling or pain in a limb- Difficulty breathing or chest pain- Rapid heartbeat- Dizziness or lightheadedness | – Persistent leg pain or heaviness- Noticeable changes in vein appearance- Skin discoloration or ulcers- Significant swelling or discomfort |
Words By Author
Understanding the differences between blood clots and varicose veins is crucial for maintaining your vascular health. While varicose veins primarily affect your legs with visible symptoms and chronic discomfort, blood clots can pose immediate and serious health risks. Recognizing the unique signs of each condition empowers you to seek timely medical attention and take proactive steps in prevention and management.
At Atlantic Cardiovascular, we specialize in diagnosing and treating both blood clots and varicose veins. Our dedicated team of experts is committed to providing personalized care to ensure your vascular health is in the best hands. If you’re experiencing symptoms or have concerns about your veins, reach out to Atlantic Cardiovascular today. Let us help you achieve healthier veins and peace of mind.