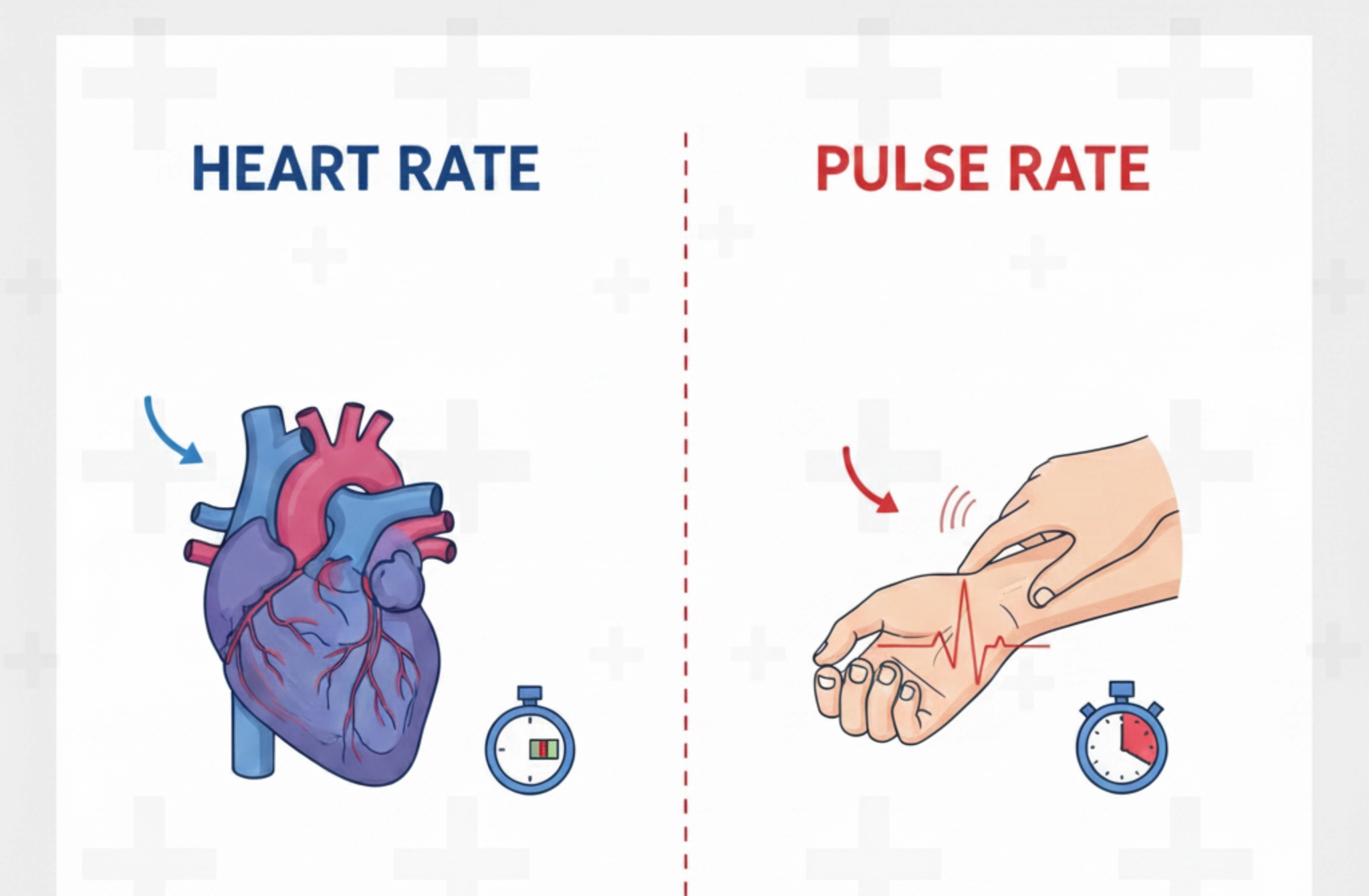
When we talk about heart health, two terms often come up: heart rate and pulse rate. While they might seem like different concepts, they are actually closely linked and often used interchangeably.
Both refer to the rhythmic beating of the heart, but the way they are measured and understood can differ.
In this blog, we’ll explore why the pulse rate is essentially the same as the heart rate, delve into how both are measured, and highlight the key factors that can influence them. Whether you’re tracking your heart’s health or simply curious about the relationship between the two, understanding this connection is essential for maintaining optimal cardiovascular function.
Let’s dive into the world of heart and pulse rate to uncover the similarities and their significance in overall health.
What is Heart Rate?
Heart rate refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute (bpm). It’s a key measure of how well your heart is functioning, delivering oxygen-rich blood to the body.
A normal heart rate varies from person to person, but typically ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute for adults at rest. It can be influenced by factors like physical activity, emotional state, and overall health, making it a valuable indicator of your cardiovascular condition.
Monitoring heart rate is important because it helps assess heart health and fitness. A resting heart rate within the normal range typically indicates a well-functioning heart, while deviations could signal potential health concerns.
Factors such as age, stress, fitness level, and physical activity can impact heart rate. For instance, regular exercise can lower your resting heart rate over time, reflecting improved heart efficiency, while stress or illness might cause a temporary increase in heart rate.
What is Pulse Rate?
Pulse rate refers to the number of times the pulse can be felt at certain points on the body, such as the wrist or neck. Each pulse corresponds to a heartbeat, as the pulse is caused by the expansion and contraction of arteries as blood is pumped from the heart.
It is often measured by feeling the radial pulse on the wrist or the carotid pulse in the neck, and it serves as an easy way to assess heart activity without the need for specialized equipment.
In most cases, pulse rate is the same as heart rate, since it reflects the number of heartbeats. However, there are situations where the pulse rate may differ from the heart rate, such as in medical conditions like arrhythmia, where the heart beats irregularly or skips beats.
Despite these differences, pulse rate is still a reliable indicator of overall heart health and can be monitored to detect potential heart issues.
Key Differences Between Heart Rate and Pulse Rate
| Aspect | Heart Rate | Pulse Rate |
| Definition | The number of times the heart beats per minute. | The number of times the pulse is felt at specific points on the body. |
| Measurement | Measured directly via ECG, heart monitor, or stethoscope. | Measured by feeling the pulse at areas like the wrist or neck. |
| Indicative of | Heart’s pumping activity and overall cardiovascular health. | The pulse felt from the blood flow generated by the heartbeats. |
| Normal Range | 60-100 beats per minute (adults at rest). | Typically matches heart rate unless there is a medical condition. |
| Situational Difference | Can remain steady or fluctuate due to exercise, stress, etc. | May differ from heart rate in cases of arrhythmia or irregular heartbeats. |
| Abnormal Patterns | Affects the heart’s rhythm and health. | Can show pulse deficits or irregularities in cases like arrhythmia. |
What is the Normal Range of Heart Rate?
Normal Resting Heart Rate:
- Typically, 60-100 beats per minute (bpm) for adults at rest.
- Reflects a healthy balance for most individuals.
Factors Affecting Heart Rate:
- Age: Resting heart rate may increase with age due to a natural decline in heart efficiency.
- Fitness Level: Highly conditioned individuals often have a lower resting heart rate due to improved heart function.
- Health Condition: Certain conditions, like thyroid issues or heart disease, can cause abnormal heart rates.
Athletes and Heart Rate:
- Athletes, especially those engaged in regular cardiovascular training, typically have a lower resting heart rate.
- A lower heart rate indicates a more efficient heart, which pumps blood with fewer beats.
What is the Normal Range of Pulse Rate?
Normal Pulse Range:
- The typical range for pulse rate is 60-100 beats per minute at rest.
- Similar to heart rate, this range reflects a healthy cardiovascular system.
Comparing Pulse to Heart Rate:
- Pulse rate is often used interchangeably with heart rate, as they usually correlate closely.
- However, factors like stress or exercise can cause fluctuations in pulse rate, even if heart rate remains stable.
- In some cases, pulse rate may be temporarily higher or lower than heart rate due to conditions like arrhythmia.
Method of Measuring Heart Rate
Manual Measurement:
- The most common method of measuring heart rate manually is by feeling the pulse at specific points on the body.
- The radial pulse is taken at the wrist, while the carotid pulse can be felt in the neck.
- To measure, simply press your fingers gently on these areas to feel the rhythmic beats, then count the number of beats for 60 seconds to calculate your heart rate.
- This method is easy to perform anywhere and can give a quick indication of heart activity.
Heart Rate Monitors:
- For a more accurate and convenient measurement, many people use heart rate monitors, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches.
- These devices use sensors to detect changes in blood flow and automatically calculate the heart rate, providing real-time data on your heart’s performance.
- Some advanced monitors can even track heart rate variability and offer insights into fitness levels and recovery times, making them useful for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Medical Devices:
- In clinical settings, heart rate is often measured using an ECG (Electrocardiogram), which provides a detailed and precise reading of the electrical activity of the heart.
- An ECG involves placing electrodes on the skin to record the heart’s electrical signals, offering a thorough analysis of heart rhythm, rate, and any potential irregularities.
- This method is used by healthcare professionals to diagnose heart conditions and monitor patients’ cardiovascular health.
Method of Measuring Pulse Rate
How to Measure Pulse:
To measure pulse, you can use your fingers to feel the rhythmic beats at several locations on the body. The most common spots include:
- Radial Pulse: Located at the wrist, just below the base of the thumb. Place your index and middle fingers on the area and count the beats for 60 seconds.
- Carotid Pulse: Found on either side of the neck, just beside the windpipe. Use your fingers to press gently to feel the pulse.
Using a Stethoscope:
Healthcare professionals often use a stethoscope to listen to the heart and measure pulse rate, especially in clinical settings. By placing the stethoscope over the chest, they can hear the heartbeat more clearly and count the beats, which is particularly useful for patients with weak or irregular pulses.
Pulse Oximeters:
Pulse oximeters are small, non-invasive devices that clip onto a finger or earlobe to measure both pulse rate and oxygen saturation levels in the blood.
Factors that Affect Heart Rate and Pulse Rate
Several factors can influence heart and pulse rates. Physical activity causes an increase in both rates as the body requires more oxygen during exercise. Emotional stress, anxiety, or excitement can also raise heart rate and pulse rate due to the body’s “fight or flight” response. Medications, such as stimulants or beta-blockers, can either speed up or slow down these rates.
Temperature also plays a role: heat increases heart rate, while cold tends to slow it down. Additionally, health conditions like fever, thyroid disorders, and heart disease can cause significant fluctuations in heart and pulse rates, requiring careful monitoring and medical attention.
Abnormal Heart and Pulse Rate Patterns
Abnormal heart and pulse rate patterns, such as tachycardia (heart rate above 100 bpm) and bradycardia (heart rate below 60 bpm), can signal underlying health issues like heart disease or electrolyte imbalances.
Arrhythmia, which causes irregular heartbeats, can also affect pulse rate and may lead to serious complications if left untreated. It’s important to seek medical help if you experience symptoms like dizziness, chest pain, or shortness of breath, as these could indicate conditions requiring immediate attention, such as arrhythmia or heart disease. Early intervention is key to preventing further health risks.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is crucial to seek medical advice if you experience warning signs such as dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, or extreme fatigue, as these could indicate serious heart or pulse rate abnormalities. If you notice continuous irregularities in your heart or pulse rate, especially when accompanied by other symptoms like fainting or discomfort, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
These could be signs of underlying health issues like arrhythmias or heart disease that require medical attention. Additionally, routine health check-ups are essential for monitoring heart and pulse health, as early detection of any irregularities can help prevent more severe complications down the road.
Regular check-ups ensure that any potential issues are caught early, allowing for more effective treatment and better overall cardiovascular health management.
- Warning Signs: Dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, or extreme fatigue.
- When to See a Doctor: Continuous irregular heart or pulse rate patterns, especially with other symptoms.
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular visits to monitor heart and pulse health and detect any issues early.
How to Improve Heart and Pulse Health Naturally
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in aerobic activities like walking, running, swimming, and cycling to strengthen the heart.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming heart-healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stress Management: Practice yoga, meditation, and mindfulness to reduce stress and maintain a healthy heart rate.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure sufficient and quality sleep to help regulate heart and pulse health.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Eliminate smoking and reduce alcohol consumption to protect heart health.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to support optimal circulation and heart function.
Bottom Line:
Maintaining a healthy heart and pulse rate is essential for long term well being and overall quality of life. Understanding how heart rate and pulse rate work together empowers you to recognize changes early and take proactive steps through regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, proper sleep, and hydration.
Just as important, routine cardiovascular check ups help identify potential issues before they become serious. If you want expert guidance, advanced diagnostics, and personalized heart care, consulting a trusted provider like Atlantic Cardiovascular can help you stay informed, protected, and confident about your heart health at every stage of life.